At Advanced Radiology, our preventive health screenings are designed to detect early signs of disease before they become bigger problems. These low-cost, non-invasive imaging exams offer peace of mind and empower you to take control of your health.
Whether you're an active adult, athlete, or managing long-term wellness, our screening services can support your goals—from monitoring bone density and heart health to identifying early warning signs of lung disease or vascular issues.
These screenings are available for self-pay without a physician’s order, using cash, credit/debit card, or HSA/FSA. Some insurance plans may cover certain screenings, but typically require a doctor’s order. If you would like to use insurance, we recommend speaking with your provider to confirm coverage. If your exam is covered, a physician referral will be needed before scheduling.
Explore each exam below to see if it's right for you!
“Of the estimated 805,000 heart attacks each year in the US, a projected 170,000 of them are silent heart attacks [attacks showing little to no symptoms], according to statistics from the American Heart Association” (American Heart Association, 2021)
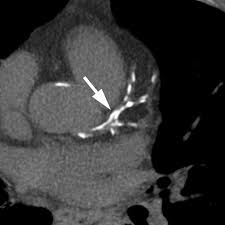
The Ultrafast CT Screening detects calcium build-up in the coronary arteries, providing a quick and non-invasive way to assess your risk for heart disease. This test identifies hardened arteries early, allowing for timely intervention with medications and lifestyle changes.
Why Get a Cardiac Calcium Score?
Heart disease is a leading cause of death, and this screening offers valuable insight into your heart’s health. By detecting early signs of coronary artery disease, it can help prevent heart attacks and allow for proactive treatment.
This screening is often recommended before more invasive procedures like stress tests or angiograms. It is especially beneficial for individuals with significant risk factors such as smoking, high cholesterol, obesity, or a family history of heart disease. The Ultrafast CT Cardiac Calcium Score is one of the most effective tools for predicting heart attack risk in otherwise healthy individuals.
What to Expect:
What Your Cardiac Score Means:
FURTHER CONSULTATION WITH A PHYSICIAN IS RECOMMENDED FOR ANY TOTAL SCORE ABOVE 0.
How Often Should I Get a Cardiac Calcium Score?
Advanced Radiology follows the recommended rescanning intervals published by The Journal of American College of Cardiology (JACC).
If your healthcare provider feels your plan of care requires more frequent scans based on your individual needs, Advanced Radiology will work with your provider to meet your needs.
When Should You Avoid a Cardiac Calcium Score Screening?
Due to the possibility of inaccurate results, it is not recommended to undergo CT Coronary Artery Calcium Screening if you have had any of the following procedures:
Golub, I, Termeie, O, Kristo, S. et al. Major Global Coronary Artery Calcium Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol Img. 2023 Jan, 16 (1) 98–117.
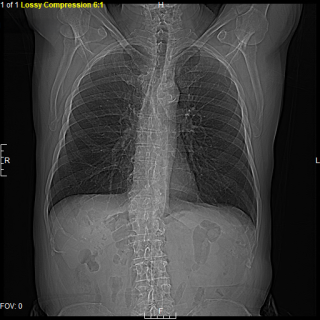
A non-invasive CT scan that uses advanced low-dose technology to detect lung abnormalities and cancer at an early, more treatable stage. The screening is far more effective than traditional chest X-rays and can identify lung tumors when they are very small.
Why Get a Lung Screening?
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the U.S. The majority of cases are diagnosed at a very late stage, which offers a low survival rate of only 5 years after diagnosis. With early detection, treatment options improve, giving you and your provider a better chance for a positive outcome.
This screening is covered by Medicare and commercial insurance companies if eligibility guidelines are met. Visit SavedByTheScan.org to see if you qualify. If you meet requirements, print out the downloadable guide and give the sheet directly to your doctor to start a conversation about next steps.
Medicare Requirements
The criteria used to determine if an individual is at high-risk of lung cancer is slightly different when looking at the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Cancer Society (ACS) standards versus Medicare. Medicare's eligibility criteria is below:
How to Schedule Your Exam:
Am I High Risk?
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Cancer Society (ACS) find those with the following criteria at high-risk:
If you are worried about lung cancer due to your history of smoking, turn your concern into answers. Contact us today to schedule your CT Lung Screening and take a proactive step towards a healthier you.
Important Reminder: Screening Is Not Prevention; Quitting Is.
While LDCT lung screening can find cancer early, it does not prevent lung cancer. Quitting smoking remains the single most powerful step you can take to protect your lung health. If you’re ready to quit, ask your primary care provider about next steps or visit smokefree.gov for expert support and free resources.
DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scan measures bone mineral density, providing an essential assessment for osteoporosis, and also calculates your BMI, which helps identify potential health risks related to body fat.
Why get a DEXA Scan?
DEXA is the only test that can diagnose osteoporosis before a broken bone occurs, allowing for early intervention and prevention. If you are a postmenopausal woman or a man age 50 and older, and have recently fractured a bone, a bone density test is highly recommended.
What to expect:
This 15-minute screening measures fat mass, lean mass, and bone health, helping you to achieve your fitness goals—whether you’re losing fat, building muscle, or improving bone density. This test is a more accurate way to assess your body's composition than BMI or BIA machines (e.g., InBody, Tanita, etc.), which assume an equal distribution of fat, muscle, and bone. This is a valuable exam for tracking fitness progress, evaluating overall health, and guiding treatment decisions when you need a more detailed assessment.
Why Get a Body Composition Test?
DEXA Body composition s considered the “gold standard” for measuring muscle, fat, and body composition, giving you a clearer picture of your health than BMI or BIA machines alone. It's particularly useful for tracking changes in fat and muscle mass to specific regions, making it ideal for those involved in fitness, wellness, or medical care. It also helps validate services like personal training, patient care, and corporate wellness programs.
What to Expect:
The CIMT test measures the thickness of the carotid artery walls to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease. It helps detect early signs of atherosclerosis, often before symptoms appear.
Why Get a CIMT Test?
Early detection of artery thickening can prevent strokes and heart disease, allowing for early intervention.
A fast, non-invasive ultrasound used to detect abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA)—a potentially life-threatening condition caused by a ballooning or weakening in the wall of the aorta, the body's largest artery. Early detection can prevent rupture and improve long-term outcomes.
Why Get an Aorta Screening?
AAA is often called a “silent killer” because symptoms rarely appear until rupture, which can lead to sudden internal bleeding and death. Screening helps detect problems before they become life-threatening.
Who Should Get Screened?
Screening is recommended for:
What to Expect
Is It Covered by Insurance?
Most insurance plans, including Medicare, cover AAA screening once for men aged 65-75 who have smoked. We also offer affordable self-pay options if you are not eligible through insurance
Take the Next Step
If you're in a high-risk group, this quick screening could save your life. Call us today to book your appointment and take control of your health.
The ABI test measures blood flow in your legs and compares it to your arms to detect peripheral artery disease (PAD)—a common condition that reduces circulation, especially in people over 60, or those with diabetes or high blood pressure.
Why Get It?
PAD increases your risk for heart attack, stroke, and limb complications. Early detection through ABI screening allows for timely treatment and lifestyle changes to improve circulation and reduce cardiovascular risks.